Relationships between number, surface area, and mass concentrations of different nanoparticles in workplaces
Abstract
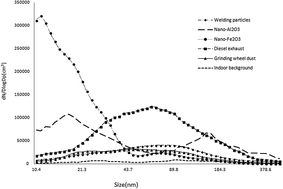
No consistent metric for measuring exposure to nanoparticles has yet been agreed upon internationally. This study seeks to examine the relationship between the number concentration (NC), surface area concentration (SAC), and mass concentration (MC) of nanoparticles in workplaces. Real-time NC20–1000 nm, SAC10–1000 nm, and respirable MC100–1000 nm were determined for different nanoparticles. Concentration ratio (CR, activity: background), exposure ranking (ER), and between-metric correlation coefficients (R) were used to analyze the relationships between the three metrics. The ratio of cumulative percentage by number (APN) and cumulative percentage by mass (APM) was used to analyze whether the nanoparticle number is predominant, as compared with the nanoparticle mass. The CRs of NC20–1000 nm and SAC10–1000 nm for different nanoparticles at the corresponding work sites were higher than those of respirable MC100–1000 nm. The ERs of NC20–1000 nm for nano-Fe2O3 and nano-Al2O3 were the same as those of SAC10–1000 nm, but were inconsistent with those of respirable MC100–1000 nm. The order of correlation coefficients between NC20–1000 nm, SAC10–1000 nm, and respirable MC100–1000 nm was: RSAC and NC > RSAC and MC > RNC and MC. The ratios of APN and APM for nano-Al2O3 and grinding-wheel particles (less than 100 nm) at the same work site were 2.03 and 1.65, respectively. NC and SAC metrics are significantly distinct from the MC in characterizing exposure to airborne nanoparticles. Simultaneous measurements of the NC, SAC, and MC should be conducted as part of nanoparticle exposure assessment strategies and epidemiological studies.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...