Simultaneous detection of endocrine disrupting chemicals including conjugates in municipal wastewater and sludge with enhanced sample pretreatment and UPLC-MS/MS†
Abstract
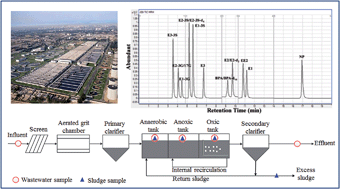
The co-existence of free and conjugated estrogens and the interference from complex matrices often lead to largely variable detected concentrations and sometimes even negative removal efficiencies of typical endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs) in wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs). In this study, a highly selective and sensitive method was developed for simultaneous extraction, elution, and detection of 12 EDCs (i.e., 4 free estrogens, 6 conjugated estrogens, and 2 phenolic compounds) in municipal wastewater and sludge. Sample pretreatment and ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry detection were optimized to improve the detection selectivity and sensitivity. The results indicate that the additional purification process was highly effective in reducing the matrix interference, and the limits of quantification reached as low as 0.04–2.2 ng L−1 in wastewater and 0.05–4.9 ng g−1 in sludge for all target EDCs. The developed method was successfully applied to explore the behavior of target EDCs in a local WWTP. The conjugates occupied a considerable portion (4.3–76.9% in molar ratio) of each related estrogen in the influent. Most of the target EDCs could not be completely removed in WWTPs, thus posing a potential threat to aquatic ecosystems.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...