A soft, multilayered lithium–electrolyte interface†
Abstract
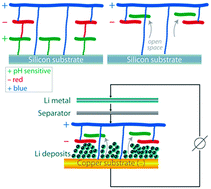
It is desirable that a thin film lithium–electrolyte interface is flexible and self-healing to accommodate the large volume expansion during lithium deposition without rupturing and impede electrolyte decomposition. The most influential area of polymer thin films is the alternating adsorption of oppositely charged polyelectrolytes popularized by the introduction of the layer-by-layer (LBL) self-assembly technique. We demonstrate that the introduction of a pH sensitive component into a nanomembrane assembled by the LBL method can have a dramatic effect on the interface governing the coulombic efficiency and morphology of lithium depositing.
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...