The formation mechanism of iron oxide nanoparticles within the microwave-assisted solvothermal synthesis and its correlation with the structural and magnetic properties
Abstract
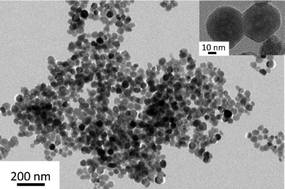
Magnetic nanoparticles based on Fe3O4 were prepared by a facile and rapid one-pot solvothermal synthesis using FeCl3·6H2O as a source of iron ions, ethylene glycol as a solvent and NH4Ac, (NH4)2CO3, NH4HCO3 or aqueous NH3 as precipitating and nucleating agents. In contrast to previous reports we reduce the synthesis time to 30 minutes using a pressurized microwave reactor without the requirement of further post-treatments such as calcination. Dramatically reduced synthesis time prevents particle growth via Ostwald ripening thus the obtained particles have dimensions in the range of 20 to 130 nm, they are uniform in shape and exhibit magnetic properties with saturation magnetization ranging from 8 to 76 emu g−1. The suggested method allows simple particle size and crystallinity tuning resulting in improved magnetic properties by changing the synthesis parameters, i.e. temperature and nucleating agents. Moreover, efficiency of conversion of raw material into the product is almost 100%.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...