Mechanical properties of zirconium alloys and zirconium hydrides predicted from density functional perturbation theory
Abstract
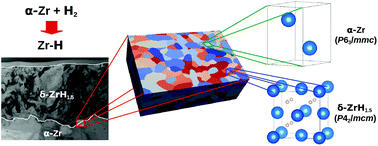
The elastic properties and mechanical stability of zirconium alloys and zirconium hydrides have been investigated within the framework of density functional perturbation theory. Results show that the lowest-energy cubic Pn![[3 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0033_0304.gif) m polymorph of δ-ZrH1.5 does not satisfy all the Born requirements for mechanical stability, unlike its nearly degenerate tetragonal P42/mcm polymorph. Elastic moduli predicted with the Voigt–Reuss–Hill approximations suggest that mechanical stability of α-Zr, Zr-alloy and Zr-hydride polycrystalline aggregates is limited by the shear modulus. According to both Pugh's and Poisson's ratios, α-Zr, Zr-alloy and Zr-hydride polycrystalline aggregates can be considered ductile. The Debye temperatures predicted for γ-ZrH, δ-ZrH1.5 and ε-ZrH2 are θD = 299.7, 415.6 and 356.9 K, respectively, while θD = 273.6, 284.2, 264.1 and 257.1 K for the α-Zr, Zry-4, ZIRLO and M5 matrices, i.e. suggesting that Zry-4 possesses the highest micro-hardness among Zr matrices.
m polymorph of δ-ZrH1.5 does not satisfy all the Born requirements for mechanical stability, unlike its nearly degenerate tetragonal P42/mcm polymorph. Elastic moduli predicted with the Voigt–Reuss–Hill approximations suggest that mechanical stability of α-Zr, Zr-alloy and Zr-hydride polycrystalline aggregates is limited by the shear modulus. According to both Pugh's and Poisson's ratios, α-Zr, Zr-alloy and Zr-hydride polycrystalline aggregates can be considered ductile. The Debye temperatures predicted for γ-ZrH, δ-ZrH1.5 and ε-ZrH2 are θD = 299.7, 415.6 and 356.9 K, respectively, while θD = 273.6, 284.2, 264.1 and 257.1 K for the α-Zr, Zry-4, ZIRLO and M5 matrices, i.e. suggesting that Zry-4 possesses the highest micro-hardness among Zr matrices.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...