Abstract
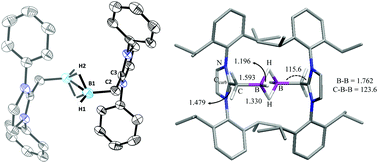
Brønsted acid HNTf2 (Tf = SO2CF3) mediated dehydrogenative hydride abstraction from (L1)BH3 (3) and (L2)BH3 (4) (L1 = IPrCH2 = 1,3-(2,6-di-isopropylphenyl)imidazol-2-methylidene (1); L2 = SIPrCH2 = 1,3-(2,6-di-isopropylphenyl)imidazolidin-2-methylidiene (2)) affords thermally stable hydride bridged mono-cationic hydrido boron compounds [{(L1)BH2}2(μ-H)](NTf2) (5) and [{(L2)BH2}2(μ-H)](NTf2) (6). Furthermore, hydride abstraction yields di-cationic hydrido boron compounds [{(L1)BH}2(μ-H)2](NTf2)2 (7) and [{(L2)BH}2(μ-H)2](NTf2)2 (8). Unique cationic boron compounds with CH2BH2(μ-H)BH2CH2 (5 and 6) and CH2BH(μ-H)2BHCH2 (7 and 8) moieties feature a 3c–2e bond and have been fully characterized. Interesting electronic and structural features of compounds 5–8 are analysed using spectroscopic, crystallographic, and computational methods.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...