1D–3D mixed-ligand frameworks with an unusual dmp topology tuned by intersection angles of isomeric benzenedicarboxylates: magnetic properties, gas-dependent calcination-thermolysis and energy storage performances†
Abstract
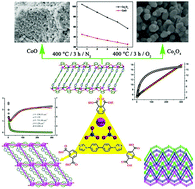
In this work, three isomeric benzenedicarboxylates, 1,2-benzenedicarboxylic acid (o-H2bdc), 1,3-benzenedicarboxylic acid (m-H2bdc), and 1,4-benzenedicarboxylic acid (p-H2bdc) have been utilized as the ancillary ligands to perform a systematic study on the structural diversity of mixed-ligand frameworks. The solvothermal reactions of Co(NO3)2 with these aromatic acids and the primary ligand 4,4′-bis(imidazolyl)biphenyl (bibp) afford three novel coordination polymers, {[Co6(bibp)3(o-bdc)6(H2O)](CH3CN)1.5}∞ (1), [Co(bibp)(m-bdc)]∞ (2), and [Co(bibp)(p-bdc)]∞ (3). Owing to the different orientations of the carboxylate groups, the benzenedicarboxylates adopt various bridging modes to connect the CoII ions into a series of 1D carboxylate∩cobalt architectures based on the 1D chain, binuclear and single-ion magnetic units, respectively. These 1D architectures are further decorated by the bibp ligand to afford a 1D belt for 1, 2D double-bridging (4,4) sheet for 2, and an unusual 3D dmp framework for 3. Significantly in 3, three equivalent frameworks are interlocked with each other to represent an unprecedented three-fold interpenetrating dmp network. The structural diversity indicates that the benzenedicarboxylate plays an essential role in the assembly of mixed-ligand frameworks, and the orientation of the carboxylate group exerts an important influence on the nucleation, dimensionality and also interpenetration. Furthermore, the magnetic properties of 1 and 2 have been studied by fitting the experimental data as possible, and the magneto-structural correlation of 2 has also been well discussed. Importantly, CoO and Co3O4 were obtained from the controllable thermolysis of crystals of 1via simple calcination treatment under different gas environments. The as-synthesized cobalt oxides display good crystallinity and appear as micro- or nanoparticles, which can be applied as supercapacitor electrodes as demonstrated by their energy storage performance in 2 M KOH electrolyte.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...