Growth characteristics of Ti-based fumaric acid hybrid thin films by molecular layer deposition†
Abstract
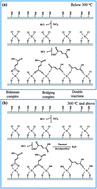
Ti-based fumaric acid hybrid thin films were successfully prepared using inorganic TiCl4 and organic fumaric acid as precursors by molecular layer deposition (MLD). The effect of deposition temperature from 180 °C to 350 °C on the growth rate, composition, chemical state, and topology of hybrid films has been investigated systematically by means of a series of analytical tools such as spectroscopic ellipsometry, atomic force microscopy (AFM), high resolution X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR). The MLD process of the Ti-fumaric acid shows self-limiting surface reaction with a reasonable growth rate of ∼0.93 Å per cycle and small surface roughness of ∼0.59 nm in root-mean-square value at 200 °C. A temperature-dependent growth characteristic has been observed in the hybrid films. On increasing the temperature from 180 °C to 300 °C, the growth rate decreases from 1.10 to 0.49 Å per cycle and the XPS composition of the film's C : O : Ti ratio changes from 8.35 : 7.49 : 1.00 to 4.66 : 4.80 : 1.00. FTIR spectra indicate that the hybrid films show bridging bonding mode at a low deposition temperature of 200 °C and bridging/bidentate mixed bonding mode at elevated deposition temperatures of 250 and 300 °C. The higher C and O amounts deviating from the ideal composition may be ascribed to increased organic incorporation into the hybrid films at lower deposition temperature and temperature-dependent density of reactive sites (–OH). The composition of hybrid films grown at 350 °C shows a dramatic decrease in C and O elemental composition (C : O : Ti = 1.97 : 2.76 : 1.00) due to the thermal decomposition of the fumaric acid precursor. The produced by-product H2O changes the structure of the hybrid films, resulting in the formation of more Ti–O bonds at high temperatures. The stability of the hybrid films against chemical and thermal treatment, and long-term storage by vacuum-packing was explored carefully. It is found that the ultrathin hybrid film can be transformed into TiO2 nanoparticles via various post deposition annealing processes with different topographies. Finally, the charge trapping ability of the hybrid film is confirmed by fabricating a charge trapping memory capacitor in which the hybrid film was inserted as a charge trapping layer.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...