An experimental-computer modeling study of inorganic phosphates surface adsorption on hydroxyapatite particles†
Abstract
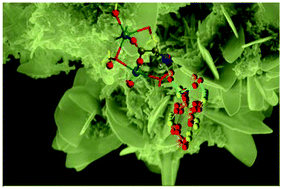
The adsorption of orthophosphate, pyrophosphate, triphosphate and a trisphosphonate onto hydroxyapatite has been examined using experiments and quantum mechanical calculations. Adsorption studies with FTIR and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopies have been performed considering both crystalline hydroxyapatite (HAp) and amorphous calcium phosphate particles, which were specifically prepared and characterized for this purpose. Density functional theory (DFT) calculations have been carried out considering the (100) and (001) surfaces of HAp, which were represented using 1 × 2 × 2 and 3 × 3 × 1 slab models, respectively. The adsorption of phosphate onto the two crystallographic surfaces is very much favored from an energetic point of view, which is fully consistent with current interpretations of the HAp growing process. The structures calculated for the adsorption of pyrophosphate and triphosphate evidence that this process is easier for the latter than for the former. Thus, the adsorption of pyrophosphate is severely limited by the surface geometry while the flexibility of triphosphate allows transforming repulsive electrostatic interactions into molecular strain. On the other hand, calculations predict that the trisphosphonate only adsorbs onto the (001) surface of HAp. Theoretical predictions are fully consistent with experimental data. Thus, comparison of DFT results and spectroscopic data suggests that the experimental conditions used to prepare HAp particles promote the predominance of the (100) surface. Accordingly, experimental identification of the adsorption of trisphosphonate onto such crystalline particles is unclear while the adsorption of pyrophosphate and triphosphate is clearly observed.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...