Comparison of photocatalytic and transport properties of TiO2 and ZnO nanostructures for solar-driven water splitting†
Abstract
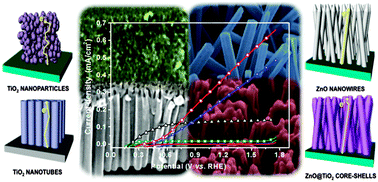
Titanium dioxide (TiO2) and zinc oxide (ZnO) nanostructures have been widely used as photo-catalysts due to their low-cost, high surface area, robustness, abundance and non-toxicity. In this work, four TiO2 and ZnO-based nanostructures, i.e. TiO2 nanoparticles (TiO2 NPs), TiO2 nanotubes (TiO2 NTs), ZnO nanowires (ZnO NWs) and ZnO@TiO2 core–shell structures, specifically prepared with a fixed thickness of about 1.5 μm, are compared for the solar-driven water splitting reaction, under AM1.5G simulated sunlight. Complete characterization of these photo-electrodes in their structural and photo-electrochemical properties was carried out. Both TiO2 NPs and NTs showed photo-current saturation reaching 0.02 and 0.12 mA cm−2, respectively, for potential values of about 0.3 and 0.6 V vs. RHE. In contrast, the ZnO NWs and the ZnO@TiO2 core–shell samples evidence a linear increase of the photocurrent with the applied potential, reaching 0.45 and 0.63 mA cm−2 at 1.7 V vs. RHE, respectively. However, under concentrated light conditions, the TiO2 NTs demonstrate a higher increase of the performance with respect to the ZnO@TiO2 core–shells. Such material-dependent behaviours are discussed in relation with the different charge transport mechanisms and interfacial reaction kinetics, which were investigated through electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. The role of key parameters such as electronic properties, specific surface area and photo-catalytic activity in the performance of these materials is discussed. Moreover, proper optimization strategies are analysed in view of increasing the efficiency of the best performing TiO2 and ZnO-based nanostructures, toward their practical application in a solar water splitting device.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...