Theoretical analysis of NMR shieldings of group-11 metal halides on MX (M = Cu, Ag, Au; X = H, F, Cl, Br, I) molecular systems, and the appearance of quasi instabilities on AuF
Abstract
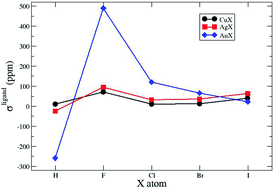
Accurate calculations of nuclear magnetic shieldings of group-11 metal halides, σ(M; MX) (M = Cu, Ag, Au; X = H, F, Cl, Br, I), were performed with relativistic and nonrelativistic theoretical schemes in order to learn more about the importance of the involved electronic mechanisms that underlie such shieldings. We applied state of the art schemes: polarization propagators at a random phase level of approach (PP-RPA); spin-free Hamiltonian (SF); linear response elimination of small component (LRESC) and density functional theory (DFT) with two different functionals: B3LYP and PBE0. The results from DFT calculations are not close to those from the relativistic polarization propagator calculations at the RPA level of approach (RelPP-RPA), in line with previous results. The spin–orbit (SO) contribution to a shielding constant is important only for MF molecules (M = Cu, Ag, Au). Different electronic mechanisms are considered within the LRESC method, bunched into two groups: core- and ligand-dependent. For the analysed shieldings the core-dependent electronic mechanisms are the most important ones; the ligand-dependent being only important for MF molecules. An out of range value for σ(Au) is found in AuF. It was previously reported in the literature, either originated in the large fluorine electronegativity together with large spin–orbit coupling contributions; or, due to Fermi-contact contributions. We argue here that such an unexpected large value is an artifact originated in the appearance of quasi instabilities, and show how to handle this apparent problem.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...