Deagglomeration of multi-walled carbon nanotubes via an organic modifier: structure and mechanism
Abstract
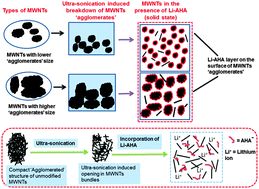
We have investigated the agglomeration behaviour of two types of multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWNTs; N-MWNTs and D-MWNTs), which have different chemical functionalities, average diameter, varying extent of agglomeration and agglomerations. The properties were altered by varying the agglomerated structure. The strength of the MWNT agglomerates was estimated via nanoindentation. The work done to indent D-MWNT agglomerates (3910.3 × 10−8 erg) was higher than for N-MWNTs agglomerates (2316.4 × 10−8 erg). An organic modifier, the Li salt of 6-aminohexanoic acid (Li-AHA), was used to deagglomerate the MWNTs in an aqueous medium. The stability of the aqueous dispersion of Li-AHA-modified MWNTs was analyzed by UV-vis spectroscopy and zeta potential measurements. An increase in Li-AHA concentration increased the dispersion of MWNTs in the aqueous medium. Furthermore, the mechanism of dispersion of the two types of MWNTs in the aqueous medium in the presence of Li-AHA was determined based on the electrostatic charge repulsion between the negatively charged species. A fluorescence-activated cell sorting technique was used to assess the debundling of MWNT agglomerates in the aqueous medium. We examined the morphology-property relationship in Li-AHA-modified MWNTs.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...