How does bile salt penetration affect the self-assembled architecture of pluronic P123 micelles? – light scattering and spectroscopic investigations†
Abstract
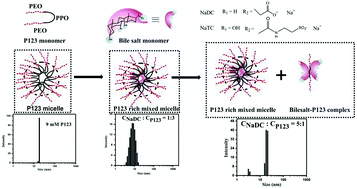
The triblock copolymer of the type (PEO)20–(PPO)70–(PEO)20 (P123) forms a mixed supramolecular aggregate with different bile salts, sodium deoxycholate (NaDC) and sodium taurocholate (NaTC), having different hydrophobicity. These mixed micellar systems have been investigated through dynamic light scattering (DLS) and other various spectroscopic techniques. DLS measurements reveal that the bile salts penetrate into the core–corona region of the P123 micelle and further addition of bile salts causes formation of a new supramolecular aggregate. Further CONTIN analysis confirms existence of two types of complexes at higher molar ratios of bile salt–P123 (>1 : 3). Due to the bile salt penetration, the polarity of the core–corona region of bile salt–P123 mixed micelle increases which results in red shift in the absorption and emission spectra of coumarin 153 (C153) and coumarin 480 (C480). The rotational diffusion of the hydrophobic probe C153 and a hydrophilic probe C480 has been investigated in these bile salt–P123 mixed systems and for both the probes a decrease in the average reorientation time has been observed. The reason behind this decrease in the average reorientation time is the increase in both polarity and hydration of the core–corona region in these mixed micelles. Moreover, these bile salt–P123 mixed micelles are characterized by fluorescence correlation spectroscopy (FCS) techniques. As hydrophobic solute 4-(dicyanomethylene)-2-methyl-6-(p-dimethylamino-styryl)-4H-pyran (DCM) resides in the core region of the bile salt–P123 mixed micelles, the translational diffusion of DCM becomes faster in these mixed micelles compared to that in pure P123 micelle. However, for cationic probe rhodamine 6G perchlorate (R6G), a totally opposite trend in the translational diffusion coefficients has been observed. Both anisotropy and FCS measurements confirm that bile salts affect the core region of the P123 micelle more than the corona region. Besides, all these characterizations confirm that more hydrophobic NaDC interacts in a better way than NaTC with the P123 micelle.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...