The solid state conversion reaction of epitaxial FeF2(110) thin films with lithium studied by angle-resolved X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy†
Abstract
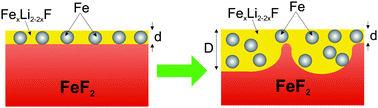
The phase evolution and morphology of the solid state FeF2 conversion reaction with Li has been characterized using angle-resolved X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (ARXPS). An epitaxial FeF2(110) film was grown on a MgF2(110) single crystal substrate and exposed to atomic lithium in an ultra-high vacuum chamber. A series of ARXPS spectra was taken after each Li exposure to obtain depth resolved chemical state information. The Li–FeF2 reaction initially proceeded in a layer-by-layer fashion to a depth of ∼1.2 nm. Beyond this depth, the reaction front became non-planar, and regions of unreacted FeF2 were observed in the near-surface region. This reaction progression is consistent with molecular dynamics simulations. Additionally, the composition of the reacted layer was similar to that of electrochemically reacted FeF2 electrodes. An intermediary compound FexLi2−2xF2, attributed to iron substituted in the LiF lattice, has been identified using XPS. These measurements provide insight into the atomistics and phase evolution of high purity FeF2 conversion electrodes without contamination from electrolytes and binders, and the results partially explain the capacity losses observed in cycled FeF2 electrodes.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...