Specific ion effects on the electrokinetic properties of iron oxide nanoparticles: experiments and simulations
Abstract
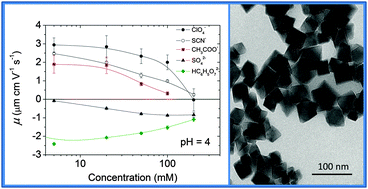
We report experimental and simulation studies on ion specificity in aqueous colloidal suspensions of positively charged, bare magnetite nanoparticles. Magnetite has the largest saturation magnetization among iron oxides and relatively low toxicity, which explain why it has been used in multiple biomedical applications. Bare magnetite is hydrophilic and the sign of the surface charge can be changed by adjusting the pH, its isoelectric point being in the vicinity of pH = 7. Electrophoretic mobility of our nanoparticles in the presence of increasing concentrations of different anions showed that anions regarded as kosmotropic are more efficient in decreasing, and even reversing, the mobility of the particles. If the anions were ordered according to the extent to which they reduced the particle mobility, a classical Hofmeister series was obtained with the exception of thiocyanate, whose position was altered. Monte Carlo simulations were used to predict the diffuse potential of magnetite in the presence of the same anions. The simulations took into account the ion volume, and the electrostatic and dispersion forces among the ions and between the ions and the solid surface. Even though no fitting parameters were introduced and all input data were estimated using Lifshitz theory of van der Waals forces or obtained from the literature, the predicted diffusion potentials of different anions followed the same order as the mobility curves. The results suggest that ionic polarizabilities and ion sizes are to a great extent responsible for the specific ion effects on the electrokinetic potential of iron oxide particles.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...