Nanoparticles of CoAPO-5: synthesis and comparison with microcrystalline samples
Abstract
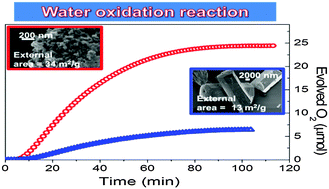
The hydrothermal synthesis of a nanosized cobalt doped aluminum phosphate CoAPO-5 (CoAPO-5-N) in a water–surfactant–organic solvent mixture (emulsion method) is reported, along with its physico-chemical characterization and comparison with a sample obtained by conventional synthesis (CoAPO-5-C). Both XRD (X-ray Diffraction) peak widths and FESEM (Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy) pictures of CoAPO-5-N are in agreement with a nanoscale structure, although the aggregation of nanoparticles occurred. EDX analysis shows a more homogeneous distribution of cobalt in CoAPO-5-N, not attainable by conventional synthesis. The specific surface area, as measured by nitrogen adsorption at 77 K, shows a limited increase in CoAPO-5-N (242 m2 g−1) with respect to CoAPO-5-C (216 m2 g−1), whereas the external surface area is almost tripled. Such a definite increase in the outer surface of CoAPO-5-N is also evidenced by the fourfold increase in the rate of a reaction only involving the exterior surface of particles, the light-driven oxidation of water by persulfate anions, as activated by the bulky Ru(bipy)32+ complex, unable to enter CoAPO-5 micropores. Two new features were also noted, adding to the knowledge of CoAPO-5 systems: (i) tetrahedral Co3+ species may coordinate ammonia molecules, assuming an octahedral configuration, as determined by UV-vis spectroscopy; (ii) Co2+ species in trigonal coordination occur, able to coordinate either CO molecules at a low temperature or ammonia (or water) at room temperature, as evidenced by IR and UV-vis spectroscopy, respectively.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...