Anisotropic gold nanoassembly: a study on polarization-dependent and polarization-selective surface-enhanced Raman scattering
Abstract
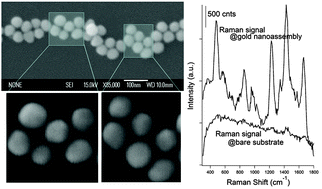
A simple one-step process was adopted to fabricate anisotropic gold nanoassemblies. Evaporation-assisted nanoparticle assembly at the meniscus was maintained in this regard. Scanning electron microscopy confirmed that the constituent nanoparticles of the anisotropic gold nanoassembly are neither in physical contact nor agglomerated; instead, they are separated by a small interparticle gap. Crystal violet was adsorbed on the anisotropic gold nanoassembly, and a large enhancement (several orders of magnitude) in surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) was observed. The assembly was thus proved to be highly SERS-active. Such an anisotropic gold nanoassembly allowed polarization dependent and polarization selective SERS experiments to be carried out. Inhomogeneous SERS and surface plasmon resonance distribution were observed along the assembly. Polarization-dependent SERS enhancement reached its highest value at in-plane polarization to the long axis, whereas polarization-selective SERS characteristics at the same spatial position showed uniform enhancement. Fluorescence emission accompanied with SERS signals was also characterized. Polarization-dependent fluorescence was enhanced at in-plane polarization to the long axis, whereas polarization-selective fluorescence was not enhanced. The experimental results were correlated and explained with three-dimensional finite definite time domain simulations as well. Such interstitial-limited gold nanoassembly provides means to realize polarized SERS characteristics for ensemble SERS measurements, which are important not only for the application-oriented fabrication of SERS-active substrates but also for understanding their feasibility in those applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...