Direct evidence for a substantive reaction between the Criegee intermediate, CH2OO, and the water vapour dimer†
Abstract
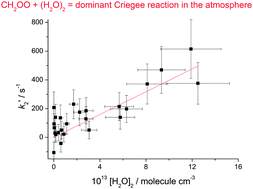
The C1 Criegee intermediate, CH2OO, reaction with water vapour has been studied. The removal rate constant shows a quadratic dependence on [H2O], implying reaction with the water dimer, (H2O)2. The rate constant, kCH2OO+(H2O)2 = (4.0 ± 1.2) × 10−12 cm3 molecule−1 s−1, is such that this is the major atmospheric sink for CH2OO.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...