Direct fabrication of nanoporous graphene from graphene oxide by adding a gasification agent to a magnesiothermic reaction†
Abstract
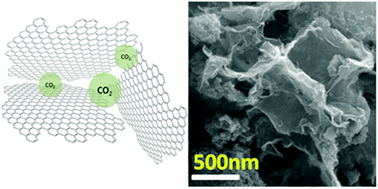
CaCO3 acts as a gasification agent during magnesiothermic reduction of graphene oxide, thus preventing the newly formed graphene from restacking. The surface area of the obtained graphene increases from 66 m2 g−1 to 603 m2 g−1 by adding CaCO3 with a high yield of ∼70% based on the carbon content in graphene oxide.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...