Bio-inspired computational design of iron catalysts for the hydrogenation of carbon dioxide†
Abstract
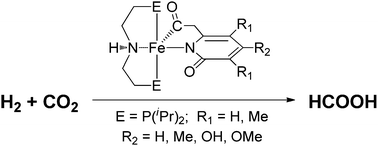
Inspired by the active site structure of monoiron hydrogenase, a series of iron complexes are built using experimentally ready-made acylmethylpyridinol and aliphatic PNP pincer ligands. Density functional theory calculations indicate that the newly designed iron complexes are very promising to catalyze the formation of formic acid from H2 and CO2.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...