Acrylate formation from CO2 and ethylene: catalysis with palladium and mechanistic insight†
Abstract
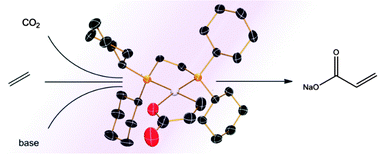
We report the first catalyst based on palladium for the reaction of CO2, alkene and a base to form sodium acrylate and derivatives. A mechanism similar to a previously reported Ni(0)-catalyst is proposed based on stoichiometric in situ NMR experiments, isolated intermediates and a parent palladalactone. Our palladium catalyst was applied to the coupling of CO2 with conjugated alkenes.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...