Kinetics and mechanism of 3,6′-disin apoylsucrose, tenuifoliside A, tenuifoliside B and tenuifoliside C degradation in aqueous solutions†
Abstract
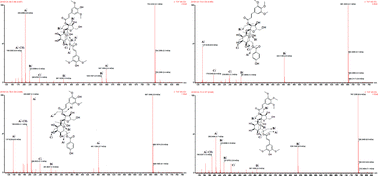
3,6′-Disin apoylsucrose, tenuifoliside A, tenuifoliside B and tenuifoliside C are the major pharmacologically active ingredients in Radix Polygalae. The hydrolytic kinetics and degradation mechanism of these compounds were studied using high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and ultra-performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry (UHPLC-Q-TOF/MS). The influence of temperature and pH on the stability of these compounds was investigated. The activation energy of 3,6′-disin apoylsucrose, tenuifoliside A, tenuifoliside B and tenuifoliside C in neutral aqueous solution (pH 6.8) was calculated to be 52.00, 42.25, 39.64, and 45.50 kJ mol−1, respectively. These four oligosaccharide esters were more susceptible to degradation under alkaline conditions. The minimum stability of 3,6′-disin apoylsucrose, tenuifoliside A, tenuifoliside B and tenuifoliside C were found at pH 10.8, and t1/2 was 0.21, 0.02, 0.17 and 0.03, respectively. The degradation products of these compounds were identified by UHPLC-Q-TOF/MS, and the degradation mechanisms were thought to be hydrolysis and isomerization, such as cis-trans isomerism, keto–enol tautomerism and optical isomerism.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...