The effect of quantum dot labeling on virus activity†
Abstract
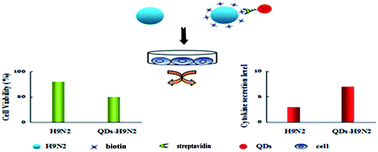
In order to evaluate the effect of quantum dot (QD) labeling on virus activity, cell viability and cytokine secretion were measured after host cells were infected by QD-labeled H9N2 and unlabeled H9N2. Our results suggested that in the process of QD labeling, biotin modification (<1 mg mL−1) had no obvious effect on virus activity. However, follow-up QD labeling enhanced the virus toxicity toward host cells and caused a high level of cytokine secretion. And our results indicate that QD-labeling is not suitable for long time tracing of viruses.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...