Sensitive electrochemical detection of vaccinia virus in a solution containing a high concentration of l-ascorbic acid†
Abstract
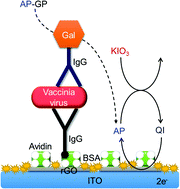
Washing processes cannot fully remove interfering species that remain on biosensing surfaces when a sample solution contains a high concentration of interfering species. This study reports an immunosensing scheme employing electroreduction-based electrochemical–chemical (EC) redox cycling that allows sensitive detection of vaccinia virus (VV) in a solution containing a high concentration of L-ascorbic acid (AA). To obtain high signal amplification, an enzymatic reaction by β-D-galactosidase (Gal) is combined with electroreduction-based EC redox cycling by an oxidant. Among the four possible oxidants (KIO3, NaClO, Ag2O, and H2O2), KIO3 shows the highest signal-to-background ratio and is chosen. During an incubation period of 10 min, Gal converts β-D-galactopyranoside into p-aminophenol (AP), which is oxidized to p-quinone imine (QI) by KIO3. When −0.05 V vs. Ag/AgCl is applied to an immunosensing electrode, QI is reduced to AP, and the regenerated AP is then reoxidized by KIO3. The electroreduction-based EC redox cycling is induced. An indium−tin oxide electrode modified with reduced graphene oxide and an applied potential of −0.05 V are used to achieve low and reproducible background currents, slow O2 reduction, and fast electroreduction of QI. KIO3 favorably converts AA into noninterfering species during the incubation period. The detection limit for VV in commercial 50% mandarin juice (AA concentration = 0.7 mM) is 4 × 103 plaque-forming unit (PFU) per mL. The new EC redox cycling scheme is promising for sensitive detection of proteins, viruses, and bacteria in solutions containing high concentrations of AA.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...