A miniaturized electrochemical assay for homocysteine using screen-printed electrodes with cytochrome c anchored gold nanoparticles†
Abstract
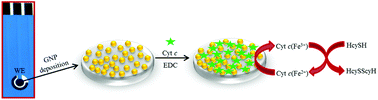
Determination of homocysteine (HcySH) is highly beneficial in human physiology and pathophysiology for diagnosis and prognosis of cardiovascular diseases (CVD). Unfortunately, the practicability of the existing methodologies for the determination of HcySH is limited in terms of sample requirements, preparation time and instrumentation cost. To overcome these limitations, we have developed a new miniaturized electrochemical assay for HcySH in which cytochrome c (cyt c) immobilized on gold nanoparticle (GNP) modified screen printed carbon electrode (SPE) is employed as a biosensing element. The electrochemical characterization of the biosensor (cyt c–GNP–SPE) shows quasi-reversible redox peaks at the potentials 0 and −0.2 V, confirming the cyt c binding. The methodology of quantification is based on the electrochemical oxidation of HcySH by the Fe3+/Fe2+ crevice of cyt c, observed at a potential of +0.56 V. Using the amperometric technique, the detection limit of HcySH is found to be 0.3 ± 0.025 μM in the linear range between 0.4 μM and 700 μM, with a sensitivity of 3.8 ± 0.12 nA μM−1 cm−2. The practical application of the present assay is validated through the measurement of HcySH in blood plasma samples and the selectivity is ensured by eliminating the impact of the common interfering biological substrates using a Nafion membrane. This biosensor shows striking analytical properties of good repeatability, reproducibility (2.85% SD) and high stability (83% of its initial current response after 4 weeks). This work paves the way for cheap, efficient and reliable point-of-care biosensors for screening one of the major causes of deaths both in the developed and developing countries.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...