A gold nanoparticle-based colorimetric probe for rapid detection of 1-hydroxypyrene in urine†
Abstract
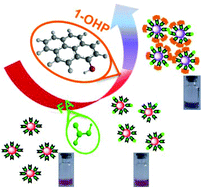
Direct and rapid detection of 1-hydroxypyrene (1-OHP) is of great importance owing to its high carcinogenicity, teratogenicity and toxicity. In this study, a simple colorimetric assay for rapid determination of 1-OHP is reported, which is based on non-crosslinking aggregation of gold nanoparticles (Au NPs) induced by 1-OHP in the presence of formic acid (FA). Initially, Au NPs were synthesized with citrate as the capping agent and exhibited red color. Subsequently, the addition of FA did not cause aggregation of Au NPs, but a proton transfer process occurred from FA to carboxylic anions on the surface of Au NPs with a decreased zeta potential. The subsequent addition of 1-OHP resulted in a further decreased zeta potential and an intensely hydrophobic environment, which led to a strong and rapid non-crosslinking aggregation of Au NPs within 5 min with the color changing from red to violet blue. Based on this principle, sensitive and selective detection of 1-OHP was achieved. The detection limit was 3.3 nM. Finally, the colorimetric assay was successfully applied to detect 1-OHP in a urine sample. This strategy provides new insights into developing colorimetric methods for on-site and real-time detection of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...