Sensitive detection of atrazine in tap water using TELISA
Abstract
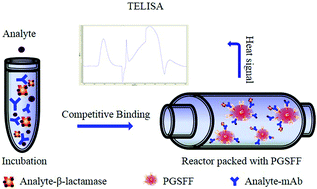
A highly sensitive flow injection analysis (FIA)-based thermal enzyme-linked immunoassay, TELISA, was developed for the rapid detection of atrazine (ATZ) in tap water. ATZ and β-lactamase-labeled ATZ were employed in a competitive immunoassay using a monoclonal antibody (mAb). After the off-column liquid-phase competition, the mAb was captured on the Protein G Sepharose™ 4 Fast Flow (PGSFF) column support material. Injected β-lactamase substrate ampicillin was degraded by the column-bound ATZ–β-lactamase, generating a detectable heat signal. Several assay parameters were optimized, including substrate concentration, flow rates and regeneration conditions, as well as the mAb and ATZ-β dilution ratios and concentrations. The assay linear range was 0.73–4.83 ng mL−1 with a detection limit of 0.66 ng mL−1. An entire heat signal requires 10 min for generation, and the cycle time is less than 40 min. The results were reproducible and stable. ATZ-spiked tap water samples exhibited a recovery rate of 103%–116%, which correlated with the UHPLC–MS/MS measurements. We attributed this significant increase in sensitivity over our previously published work to the following factors: (i) the capture of already-formed immune complexes on the column via immobilized Protein G, which eliminated chemical immobilization of the antibody; (ii) off-column preincubation allows the formation of immune complexes under nearly ideal conditions; and (iii) multiple buffers can be used to, in one case, enhance immune-complex formation and in the other to maximize enzymatic activity. Furthermore, the scheme creates a universal assay platform in which sensing is performed in the off-column incubation and detection after capture in the enzyme thermistor (ET) detector, which opens up the possibility of detecting any antigen for which antibodies were available.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...