Self-calibrating highly sensitive dynamic capacitance sensor: towards rapid sensing and counting of particles in laminar flow systems
Abstract
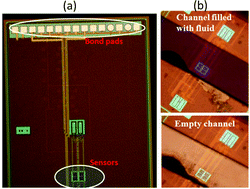
In this report we propose a sensor architecture and a corresponding read-out technique on silicon for the detection of dynamic capacitance change. This approach can be applied to rapid particle counting and single particle sensing in a fluidic system. The sensing principle is based on capacitance variation of an interdigitated electrode (IDE) structure embedded in an oscillator circuit. The capacitance scaling of the IDE results in frequency modulation of the oscillator. A demodulator architecture is employed to provide a read-out of the frequency modulation caused by the capacitance change. A self-calibrating technique is employed at the read-out amplifier stage. The capacitance variation of the IDE due to particle flow causing frequency modulation and the corresponding demodulator read-out has been analytically modelled. Experimental verification of the established model and the functionality of the sensor chip were shown using a modulating capacitor independent of fluidic integration. The initial results show that the sensor is capable of detecting frequency changes of the order of 100 parts per million (PPM), which translates to a shift of 1.43 MHz at 14.3 GHz operating frequency. It is also shown that a capacitance change every 3 μs can be accurately detected.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...