Injectable biodegradable hydrogels and microgels based on methacrylated poly(ethylene glycol)-co-poly(glycerol sebacate) multi-block copolymers: synthesis, characterization, and cell encapsulation†
Abstract
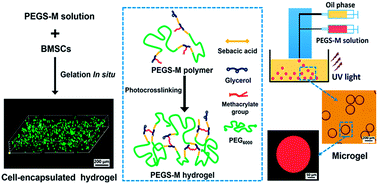
Poly(glycerol sebacate) (PGS) has great potential for application in tissue engineering due to its good biocompatibility, tunable mechanical properties and controlled biodegradability. However, the complex thermal curing process and poor water uptake capacity of PGS-based biomaterials limit their use directly in tissue and cell encapsulation in situ applications. We present novel injectable photocurable biodegradable hydrogels based on methacrylated poly(ethylene glycol)-co-poly(glycerol sebacate) copolymers (PEGS-M), which show good hydration properties and an easy in situ gelation process by photopolymerization under physiological conditions. The swelling ratio, mechanical properties and biodegradation behavior of PEGS-M hydrogels were demonstrated to be controllable by tuning the degree of methacrylation of the copolymer. We further fabricated monodisperse spherical PEGS-M microgels with different diameters ranging from 154.2 ± 2.0 to 403.9 ± 3.6 μm via a microfluidic chip. Rabbit bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) encapsulated in situ in the PEGS-M hydrogel by photocrosslinking maintained their viability for two weeks, demonstrating the good biocompatibility of PEGS-M hydrogels for long-term cell cultivation. All these data suggest that cell-encapsulated PEGS-M hydrogels and microgels have potential application as injectable tissue engineering scaffolds.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...