Intracellular temperature sensing by a ratiometric fluorescent polymer thermometer†
Abstract
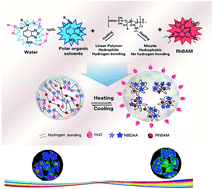
Intracellular temperature imaging could help to understand diverse biological reactions and functions in living cells. Herein, we report a nanothermometer based on ratiometric fluorescent polymers (RFPs) synthesized by the living/controlled reversible addition–fragmentation transfer polymerization method for intracellular temperature sensing. The thermometer was composed of a thermo sensitive polymer, a polarity sensitive fluorescent dye and a thermo insensitive fluorescent dye. With the increasing temperature, the fluorescent intensity of RFPs increased because of the fluorescent intensity enhancement of the polarity sensitive fluorescent dye induced by the self assembling of the thermo sensitive polymer. The prepared RFPs exhibited a fluorescence “turn-on” response at higher temperature. We further investigated the simultaneous temperature sensing and the ratiometric imaging of temperature variations associated with biological processes in living cells using this novel ratiometric probe. The polymer based ratiometric fluorescent thermometer can be used to precisely measure the temperature in living cells, and shows great potential in spatio-temporal temperature sensing down to the nanoscale within biological systems.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...