ROS-cleavable proline oligomer crosslinking of polycaprolactone for pro-angiogenic host response†
Abstract
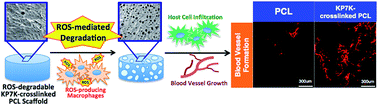
A reactive oxygen species (ROS)-degradable scaffold is fabricated by crosslinking biocompatible, hydrolytically-degradable poly(ε-caprolactone) (PCL) with a ROS-degradable oligoproline peptide, KP7K. The ROS-mediated degradability triggers favorable host responses of the scaffold including improved cell infiltration and angiogenesis in vivo, indicating its unique advantages for tissue engineering applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...