Development of a spatiotemporal method to control molecular function by using silica-based photodegradable nanoparticles
Abstract
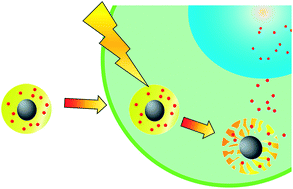
To effectively and safely use molecules, it is important to be able to control the timing and site of molecule activation. We developed a spatiotemporal method to control molecular function by using silica-based photodegradable nanoparticles that can be prepared under mild conditions. The function of various molecules, such as rhodamine B, Nile blue A, propidium iodide (PI), and rhodamine 110, bis-(N-CBZ-L-arginine amide), dihydrochloride (BZAR), was restricted by wrapping in the network structure of the nanoparticle gel. The encapsulated molecule was released from the gel by the light stimulus and its function was restored. Hence, this technique is applicable to the functional control of various molecules. The PI-encapsulated nanoparticles were internalized by the cells after being conjugated with the cell membrane permeability peptide, octaarginine, and were localized to the cytoplasm. Short-term irradiation (20 s) induced PI release from the nanoparticles and the rapid movement (less than 2 min) of the released PI to the nucleus. These nanoparticles are thus useful tools for the spatiotemporal control of various molecular functions because they permit the quick and transient release of encapsulated molecules after short-term irradiation and can be prepared under mild conditions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...