Efficient enrichment of glycopeptides using phenylboronic acid polymer brush modified silica microspheres†
Abstract
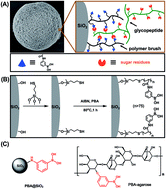
For the development of rapid glycopeptide enrichment materials, conventional monolayer phenylboronic acid (PBA) based materials inevitably encounter many problems, such as low loading efficiency, long incubation time, and unsatisfactory selectivity. Extending the materials from a 1D monolayer to a 3D polymeric matrix will be one of the best candidates tackling these problems. In this work, a PBA-based polymer material (denoted as polyPBA@SiO2) was developed, in which flexible PBA polymer brushes were immobilized on the surface of silica microspheres, constructing an ideal platform for the efficient enrichment of glycopeptides. This material exhibits stronger interaction with glycopeptides in a higher concentration of organic solvent than in aqueous solution, resulting in the high binding capacity of 60 mg g−1. Moreover, higher selectivity for glycopeptides can be achieved with polyPBA@SiO2 than with both monolayer PBA modified silica and commercial PBA-agarose. These unique features of polyPBA@SiO2 could be attributed to the synergistic effect of polyvalent interactions provided by the polymer brush, specific interaction between PBA and glycopeptides and suppression of the non-specific binding of non-glycopeptides under high ACN concentration.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...