Enhancing sensitivity in a piezoresistive cantilever-based label-free DNA detection assay using ssPNA sensor probes†
Abstract
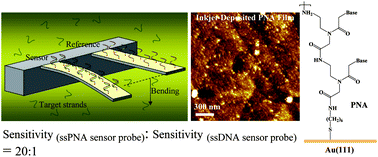
In this work, a strategy for enhancing sensitivity in a label-free DNA detection assay, where the basic operational principle involves detection of the net surface stress induced bending motion of a piezoresistive microcantilever, upon target-binding, has been presented. A microcantilever array that allows experiments using sensor–reference configuration has been employed, where the cantilevers have been functionalized by inkjet printing technology, using short nucleic acid sequences of similar length (here, 12-mer), on both the sensor and the reference cantilevers. It is shown that application of the single stranded peptide nucleic acids (PNA), having non-ionic peptidic backbone, as the sensor probes improves the assay sensitivity about twenty times, even to the level of single base mismatch discrimination, compared to the DNA counterparts. We propose that the significantly improved performance of the PNA-based assay could be due to the orientational advantage of PNA probes as offered when a self-assembled ordered PNA structure is formed. Since the piezoresistive cantilever based method offers a practical means for target detection by rapid monitoring of the recognition events in fluid in real time, and importantly, since PNA is nuclease-resistant, this step of advancement may motivate future endeavours for detection of nucleic acid sequences in complex body fluid mimics.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...