Intermediate band in the gap of photosensitive hybrid gel based on titanium oxide: role of coordinated ligands during photoreduction†
Abstract
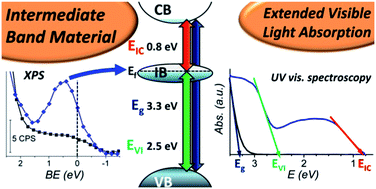
UV light induced chemical modifications of a new hybrid organic–inorganic gel, based on titanium oxide and obtained by a soft chemistry method, are studied by XPS and UV-visible spectroscopy. XPS experiments, with an in situ UV illumination design, were performed in order to study the different chemical modifications of the gel. The Ti4+ to Ti3+ reduction, as well as the associated change in the ligands coordinating titanium cations, are accompanied by a deprotonation of the molecules in the vicinity of the inorganic part. In the meantime, an intermediate band arises in the gap just below the Fermi level. The appearance of this band correlates with the light absorption properties of the gel as measured by UV-visible spectroscopy. Following on from these experiments, a complete band diagram of the electronic structure is proposed in order to clarify the position of this intermediate band. These distinctive properties suggest that the nanostructured hybrid gel could be used as a new class of intermediate band material that can be synthesized at low cost for photovoltaic applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...