Controllable growth of graphene/Cu composite and its nanoarchitecture-dependent electrocatalytic activity to hydrazine oxidation†
Abstract
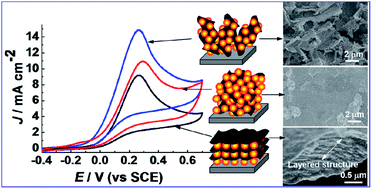
Graphene is a promising support for nanosized electrocatalysts, however the conventional stacking arrangement of its graphene sheets substantially decreases the catalytic sites on the catalyst. We report here the fabrication of a graphene/Cu electrocatalyst by the simple cyclic voltammetric electrolysis of graphene oxide (GO) and copper ethylenediamine tetraacetate (Cu–EDTA), and find that the electrochemically reduced GO (RGO) and Cu nanoparticles can be sequentially self-assembled into layer-by-layer, 3D sandwich-type, and homogenous architectures as the concentration ratio of Cu–EDTA/GO increases. The 3D sandwich-type RGO/Cu composite (S-RGO/Cu) shows RGO sheets decorated with Cu nanoparticles which stand nearly perpendicular on the electrode, leading to a significant increase in the electrochemically accessible surface area (0.685 cm2) relative to those of the horizontal layer-by-layer RGO/Cu composite (0.147 cm2) and the homogenous RGO/Cu composite (0.265 cm2). Stemming from its high electrochemical surface area, the S-RGO/Cu composite exhibits a high electrocatalytic activity in hydrazine oxidation in terms of current density and overpotential. Mechanistic analysis of the electrode reactions reveals the reaction pathways of hydrazine on RGO/Cu are closely related to the electrochemical surface area of the RGO/Cu electrocatalyst. The correlation between the architectures and their performances in electrocatalysis presented here can guide the design of novel structures with enhanced properties.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...