Correlating surface cation composition and thin film microstructure with the electrochemical performance of lanthanum strontium cobaltite (LSC) electrodes
Abstract
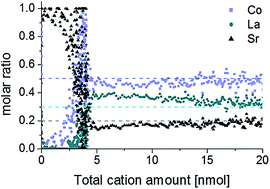
La0.6Sr0.4CoO3−δ thin films of varying thicknesses (20–170 nm) were prepared by pulsed laser deposition on yttria-stabilized zirconia (100) substrates, and their electrochemical electrode performance was correlated with the chemical surface composition and microstructure (e.g. porosity, surface area). The surface cation composition was analyzed by an atomic etching procedure with on-line inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry detection. The surface sensitivity of the method was increased by dynamically switching the etching reagent during the on-line analysis and quantitative results for even the top atomic layer were obtained. A water-soluble Sr-rich surface species could be quantified on top of the LSC films and in combination with electrochemical analysis of the films by impedance spectroscopy an improved understanding of the surface exchange resistance could be obtained. Microstructural features such as the effective porosity of the films became accessible by a combination of these methods.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...