New Si–O–C composite film anode materials for LIB by electrodeposition
Abstract
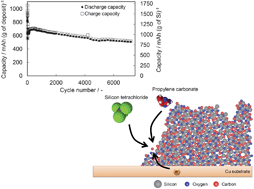
Silicon is one of the most promising materials for lithium secondary battery anodes. However, silicon anodes have a critical drawback to their practical application, which is capacity degradation due to pulverization of the active material by the large volume change of silicon during charge–discharge cycles. This paper reviews recent studies on silicon-based anodes that have attempted to overcome this poor cycle durability through structural control such as through thin films, porous structures, core–shell structures, and by alloying with other metals, and by application of proper binders. Among them, binder-free Si–O–C composite films prepared by electrodeposition exhibit outstanding cycle durability. The origin of this excellent durability is discussed in depth from the standpoint of chemical and morphological changes. Consequently, the combination of active materials such as Si and Li2Si2O5 and inactive materials such as Li2O, Li2CO3, and organic compounds is suggested to result in outstanding properties as a lithium secondary battery anode.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...