Tribological studies of stearic acid-modified CaCu2.9Zn0.1Ti4O12 nanoparticles as effective zero SAPS antiwear lubricant additives in paraffin oil†
Abstract
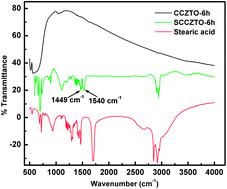
Stearic acid modified ceramic nanoparticles SCCZTO-6 h, SCCZTO-8 h and SCCZTO-12 h of average sizes 60, 80 and 90 nm were prepared from CCZTO-6 h, CCZTO-8 h and CCZTO-12 h respectively (where CCZTO represents CaCu2.9Zn0.1Ti4O12; 6 h, 8 h and 12 h are the sintering times). The SCCZTO nanoparticles have been characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Tribological behavior of these nanoparticles in liquid paraffin oil has been evaluated using a four-ball lubricant tester and compared with conventional high SAPS containing zinc dialkyldithiophosphates (ZDDP). All antiwear tests have been performed using an optimized concentration of the SCCZTO nanoparticles (1% w/v) by varying the load for a 30 min test duration and by varying the test durations at 392 N load. Various tribological parameters such as mean wear scar diameter (MWD), friction coefficient (μ), mean wear volume (MWV), running-in, steady-state and overall wear rates show that all the SCCZTO nanoparticles act as efficient antiwear additives and possess a high load carrying capacity. The best tribological behavior is shown by SCCZTO-6 h, followed by SCCZTO-8 h and then SCCZTO-12 h. The surface morphology and roughness of the wear scar have been studied by Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) and Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) respectively. AFM and SEM micrographs of the wear scar in the presence of SCCZTO-6 h and SCCZTO-8 h at 392 N applied load for a 90 min test duration show a drastic decrease in surface roughness. Energy-Dispersive X-ray (EDX) analysis of the worn surface under similar experimental conditions in the presence of SCCZTO-6 h nanoparticles exhibits the presence of calcium, copper, zinc, titanium and oxygen on the worn steel surface indicating tribosinterization and/or adsorption of the additive on the rubbing surface resulting in the formation of a strong tribofilm. X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) of the tribofilm shows the presence of CaO, CuO, Cu2O, TiO2, Fe2O3 and adsorbed carbon in the form of –C–C– and –C(O)O– moieties.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...