Thermoresponsive PNIPAAM bottlebrush polymers with tailored side-chain length and end-group structure†
Abstract
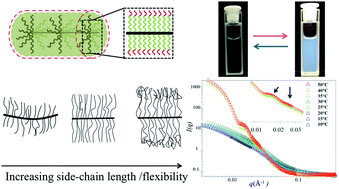
We explore the phase behaviour, solution conformation, and interfacial properties of bottlebrush polymers with side-chains comprised of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (PNIPAAM), a thermally responsive polymer that exhibits a lower critical solution temperature (LCST) in water. PNIPAAM bottlebrush polymers with controlled side-chain length and side-chain end-group structure are prepared using a “grafting-through” technique. Due to reduced flexibility of bottlebrush polymer side-chains, side-chain end-groups have a disproportionate effect on bottlebrush polymer solubility and phase behaviour. Bottlebrush polymers with a hydrophobic end-group have poor water solubilities and depressed LCSTs, whereas bottlebrush polymers with thiol-terminated side-chains are fully water-soluble and exhibit an LCST greater than that of PNIPAAM homopolymers. The temperature-dependent solution conformation of PNIPAAM bottlebrush polymers in D2O is analyzed by small-angle neutron scattering (SANS), and data analysis using the Guinier–Porod model shows that the bottlebrush polymer radius decreases as the temperature increases towards the LCST for PNIPAAM bottlebrush polymers with relatively long 9 kg mol−1 side-chains. Above the LCST, PNIPAAM bottlebrush polymers can form a lyotropic liquid crystal phase in water. Interfacial tension measurements show that bottlebrush polymers reduce the interfacial tension between chloroform and water to levels comparable to PNIPAAM homopolymers without the formation of microemulsions, suggesting that bottlebrush polymers are unable to stabilize highly curved interfaces. These results demonstrate that bottlebrush polymer side-chain length and flexibility impact phase behavior, solubility, and interfacial properties.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...