Programmable co-assembly of oppositely charged microgels†
Abstract
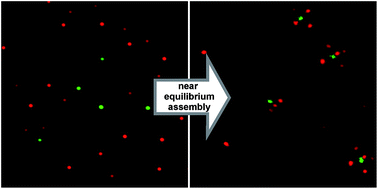
Here we report the development of an aqueous, self-assembling system of oppositely charged colloids leading towards particle arrangements with controlled order. The colloidal system consists of two types of particles, each consisting of refractive index matched colloidal core–shell microgel particles, which are either negatively charged or amphoteric. By slowly decreasing the pH of our system below the isoelectric point of the amphoteric particles, changing their net charge from negative to positive, the co-assembly of the colloids is induced. By using different buffer concentrations, we gain temporal and kinetic control over the acidification process and thus the ability to program the co-assembly of the two particles species.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...