Foams stabilised by mixtures of nanoparticles and oppositely charged surfactants: relationship between bubble shrinkage and foam coarsening†
Abstract
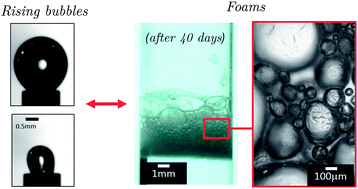
We have studied foams stabilised by surfactant-decorated nanoparticles adsorbed at the bubble surfaces. We show that the controlled compression of a single bubble allows one to understand the coarsening behavior of these foams. When bubbles are compressed, the particles become tightly packed in the surface layer. They lose their mobility, and the interface becomes solid-like when the jammed state is reached. Further compression leads to interfacial buckling characterised by crumpled surfaces. We find that the surface concentration of particles at which the jamming and the buckling transitions occur are independent of the surfactant concentration. This is a surprising feature. It suggests that the surfactants are mandatory to help the particles adsorb at the interface and that they change the equilibrium surface concentration of the decorated particles. But they do not affect the surface properties once the particles are adsorbed. We measured the compression elastic modulus of the surface in the jammed state and found it to be compatible with the Gibbs condition for which the spontaneous dissolution of bubbles is arrested. Due to this effect, the coarsening process of a foam composed of many close-packed bubbles occurs in two steps. In the first step, coarsening is slow and coalescence of the bigger bubbles is observed. In the second step, a number of very small bubbles remains, which exhibit crumpled surfaces and are stable over long times. This suggests that foam coarsening is arrested once the smallest bubbles become fully covered after the initial shrinking step.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...