Ormosil nanoparticles as a sustained-release drug delivery vehicle†
Abstract
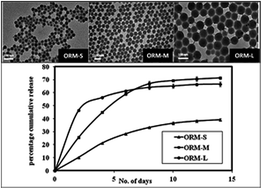
Silica-based nanoparticles are well known for their ease of synthesis, structural robustness, resistance to biofouling, enhanced storage stability, and multimodality. Organically modified silica (ormosil) nanoparticles are a special type of hybrid nanoparticle known for encapsulating/conjugating active agents for applications such as in photodynamic therapy (PDT), gene therapy and diagnostic imaging. Herein, we report the use of ormosil nanoparticles as a sustained release drug delivery vehicle, using the well-known anticancer and fluorescent drug doxorubicin (Dox). These drug/dye loaded nanoparticles have been synthesized within an oil-in-water microemulsion medium, and characterized for their size, shape, porosity, and optical properties. Nanoencapsulation significantly enhanced the optical stability of a dye against chemical quenching. Particle-size variation could be achieved by changing the amount of co-surfactant. However, size variation did not affect their pore size. The release pattern of encapsulated drug was found to depend on the size of the nanoparticles, with optimal drug release observed for the 50 nm particles at about 70% in a sustained manner over two weeks. Confocal bioimaging was used to demonstrate the differential pattern of cellular uptake of the free and nanoencapsulated drugs, as the sub-cellular distribution of nanoencapsulated Dox is guided by the nanoparticles distributing throughout the cytosol. Cell viability (MTS) and soft-agar colony formation assays in vitro have confirmed the cytotoxic effects of the drug loaded nanoparticles, but not of the blank nanoparticles. The results indicate that ormosil nanoparticles can act as a sustained release vehicle of potent lipophilic anticancer drugs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...