Mn2+ ion influenced optical and photocatalytic behaviour of Mn–ZnS quantum dots prepared by a microwave assisted technique†
Abstract
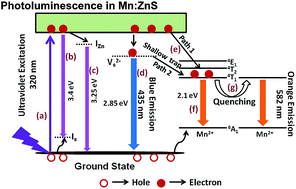
Fluorescent zinc blende structured pure and Mn2+ ion doped ZnS (Mn–ZnS) quantum dots were prepared via a rapid microwave assisted technique without any surfactants and their photocatalytic activity was tested for the photodegradation of methyl orange dye under UV light irradiation. They were characterized by X-ray diffraction, FE-SEM, UV-Vis and photoluminescence spectroscopies, XRF and BET surface area analysis. The Mn–ZnS quantum dots possessed a cubic blende crystal structure without any impurity phases. The absorption maximum by UV-Vis spectroscopy showed a blue shift with increasing Mn2+ content. Photoluminescence of Mn–ZnS was obtained as a result of combined broad blue emission from sulfur vacancies existing in the ZnS host and orange emission from the 4T1–6A1 transition of Mn2+. The relative intensity of blue to orange emissions was found to be quenched with increasing Mn2+ ion concentration. Methyl orange dye was photodegraded by Mn–ZnS quantum dots effectively up to a doping level of 4.28% Mn2+ and further increase in Mn2+ decreased the photocatalytic activity. Detailed mechanisms of photoluminescence and photocatalytic activity were proposed and discussed. The results suggested that the Mn–ZnS material is a potential candidate for photocatalytic applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...