A molecular level understanding of interaction between FTY720 (Fingolimod hydrochloride) and DMPC multilamellar vesicles†
Abstract
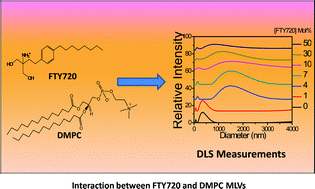
This work focuses on the molecular level understanding of interaction between FTY720 (Fingolimod hydrochloride) and dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine (DMPC) multilamellar vesicles (MLVs) as a drug molecule carrier by investigating the structural changes, solubilisation effect and thermotropic phase behaviour. Three different techniques like dynamic light scattering (DLS), differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and fluorescent molecular probe based techniques were used to study the effect of FTY720 on DMPC MLVs. DLS studies showed that FTY720 induces a marked change in the DMPC MLVs' structure and solubilises the lipid membrane with the increase in concentration of FTY720. DSC and temperature dependent fluorescence intensity studies of 1-naphthol showed that FTY720 broadens and shifts the phase transition temperature of the DMPC MLVs to a lower temperature. This is in contrast to the effect of the sphingosine which is a structural analogous to FTY720. Fluorescence anisotropy study of 1,6-diphenyl-1,3,5-hexatriene (DPH) also revealed the above phenomena. Fluorescence lifetime decay analysis of 1-naphthol suggested that incorporation of FTY720 causes a redistribution of 1-naphthol molecules between the core and interfacial regions of the membrane.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...