Microfluidic long-term differential oxygenation for bacterial growth characteristics analyses†
Abstract
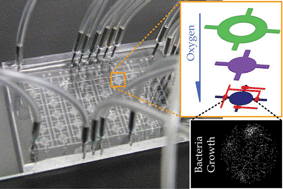
Dissolved oxygen is a critical micro-environmental factor to determine the growth characteristics of bacteria, such as cell viability, migration, aggregation and metabolic processes. Here, we report a microfluidic long-term oxygenator which can support high-throughput parallel cell cultures under multiple defined oxygenation conditions (0–42 ppm). An array of oxygen–nitrogen gas micro-mixers is developed and fabricated in the device to generate stable oxygen concentrations for the oxygenation process. A water-jacket layer located between the gas layer and the cell culture chamber is applied to block evaporation and maintain the conditions of the culture media in the chamber. Furthermore, we perform simulations and experiments to investigate the functions of the gas mixers and the water jackets. We also conduct culture experiments to study the long-term growth (up to one week) and aggregation of three selected dental bacteria (Streptococcus mutans, Actinomyces viscosus and Fusobacterium nucleatum) under ranges of oxygenation conditions. These particular results can provide important insights into their roles in dental biofilm formation. Overall, this work demonstrates that the long-term microfluidic oxygenation approach can effectively regulate defined dissolved-oxygen levels in cell microenvironments. Importantly, this oxygenation approach can be further applied to general long-term analyses of cells for their behavioral, metabolic and genetic responses, and their biofilm formation processes.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...