CHx adsorption (x = 1–4) and thermodynamic stability on the CeO2(111) surface: a first-principles investigation
Abstract
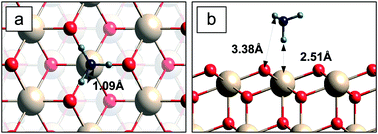
We present an ab initio investigation of the interaction between methane, its dehydrogenated forms and the cerium oxide surface. In particular, the stoichiometric CeO2(111) surface and the one with oxygen vacancies are considered. We study the geometries, energetics and electronic structures of various configurations of these molecules adsorbed on the surface in vacuum, and we extend the analysis to realistic environmental conditions. A phase diagram of the adsorbate–surface system is constructed and relevant transition phases are analyzed in detail, showing the conditions where partial oxidation of methane can occur.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...