The synthesis of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID)–lantadene prodrugs as novel lung adenocarcinoma inhibitors via the inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), cyclin D1 and TNF-α-induced NF-κB activation†
Abstract
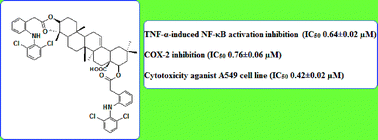
The ester conjugates of potent nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) inhibitors with cyclooxygenase (COX) inhibiting non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) present a novel approach towards cancer treatment. The ester prodrugs of pentacyclic triterpenoid 3β,22β-dihydroxy-olean-12-en-28-oic acid (4) with different NSAIDs were synthesized for the dual inhibition of NF-κB and COX-2. The results indicated that the lead compound 14 suppressed the tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced (TNF-α-induced) activation of NF-κB by inhibiting the inhibitor of the nuclear factor-kappa B kinase (IKK) activation, the inhibitor of the nuclear factor-kappa B alpha (IκBα) degradation and at the same time, it down-regulated the NF-κB mediated protein expression of COX-2 and cyclin D1. Furthermore, compound 14 inhibited lung adenocarcinoma A549 cell proliferation in a dose dependent manner and was found to be 50 folds more active than cisplatin in terms of IC50. Compound 14 was also found to be stable in an acidic pH, while it hydrolyzed readily in human plasma to release the active promoieties. From the results it can be inferred that the lantadene–NSAID prodrugs are promising anticancer candidates against lung cancer with a dual inhibition capability against both NF-κB and COX-2.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...