Pyrene-labeled pyrrolidinyl peptide nucleic acid as a hybridization-responsive DNA probe: comparison between internal and terminal labeling†
Abstract
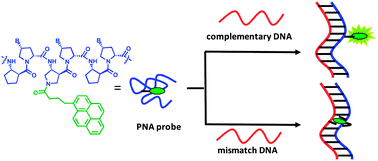
Nucleic acids or nucleic acid analogues carrying an environment sensitive fluorophore that can change optical properties in response to hybridization with complementary DNA or RNA targets are potentially useful as self-reporting hybridization probes that do not require a quencher. In this study, pyrrolidinyl peptide nucleic acids (acpcPNA) carrying a pyrene label at terminal, or internal positions were synthesized and their fluorescence properties investigated. Significant fluorescence increases, between 2.9 and 73 fold, were observed only with internally pyrene-labeled acpcPNA upon hybridization with complementary DNA under a variety of sequence contexts. Hybridization with mismatched DNA targets yielded mostly unchanged or decreased fluorescence, depending on the type and position of the mismatch base. Non-specific fluorescence increase due to the presence of a mismatch located away from the pyrene label could be eliminated by digestion with S1 nuclease, which allows unambiguous discrimination between complementary and all single mismatched DNA targets. The terminally pyrene-labeled acpcPNA showed a much smaller fluorescence change upon hybridization with both complementary and mismatched DNA targets, and the change was in the opposite direction to the internally pyrene-labeled acpcPNA. These results were rationalized by the use of molecular dynamics simulations, which suggested that the pyrene label adopts a different conformation when located at different positions of the acpcPNA probes.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...