Micellar transitions in catanionic ionic liquid–ibuprofen aqueous mixtures; effects of composition and dilution†
Abstract
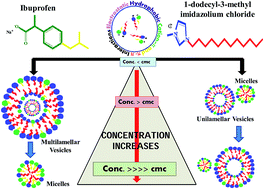
The present study aims to develop a basic understanding of the molecular interactions of an anti-inflammatory drug, ibuprofen (Ibu), with a surface active ionic liquid (IL), 1-dodecyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride (C12mimCl), in aqueous medium, owing to their utility as the components of pharmaceutically active ionic liquids. Various techniques such as surface tension, steady-state fluorescence, UV-visible absorption, dynamic light scattering and 1H NMR measurements have been employed to provide comprehensive knowledge of the C12mimCl –Ibu interactions. The interactions between the ionic liquid and drug molecules have been found to be highly synergistic both in the mixed micelles as well as in the mixed monolayer due to the formation of catanionic mixtures. These mixtures are seen to display enhanced micellization and adsorption tendencies and varied aggregate assemblies in aqueous medium determined by the amphiphile mixing ratio and the total mixture concentration. The dilution induced transformation of smaller micelles to larger aggregates is ascribed to the solubility mismatch between the two components. Quantitative evaluation of the process of interaction between Ibu and the ILs has been done in terms of various quenching and binding parameters exploiting the fluorescence measurements. The formation of highly surface active catanionic complexes (C12mim+Ibu−) of 1 : 1 stoichiometry stabilized largely by a combination of electrostatic, hydrophobic, cation–π and π–π interactions has been well established through spectroscopic investigations.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...